Featured Images
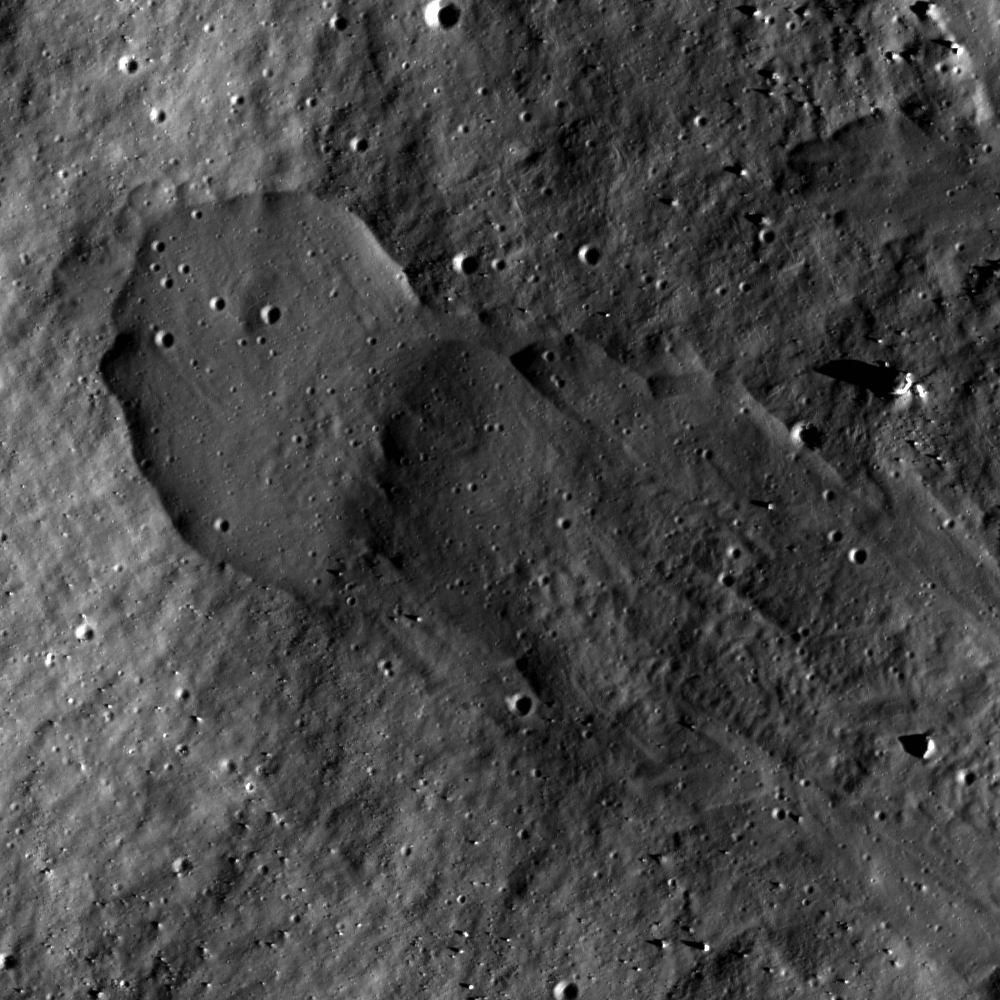

Outside of Giordano Bruno
Ejecta flows outside of Giordano Bruno crater. Sun direction is from right to left. Image number M161646501R, incidence angle 71°, image scale 0.55 m/pixels [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 25 Aug 2011
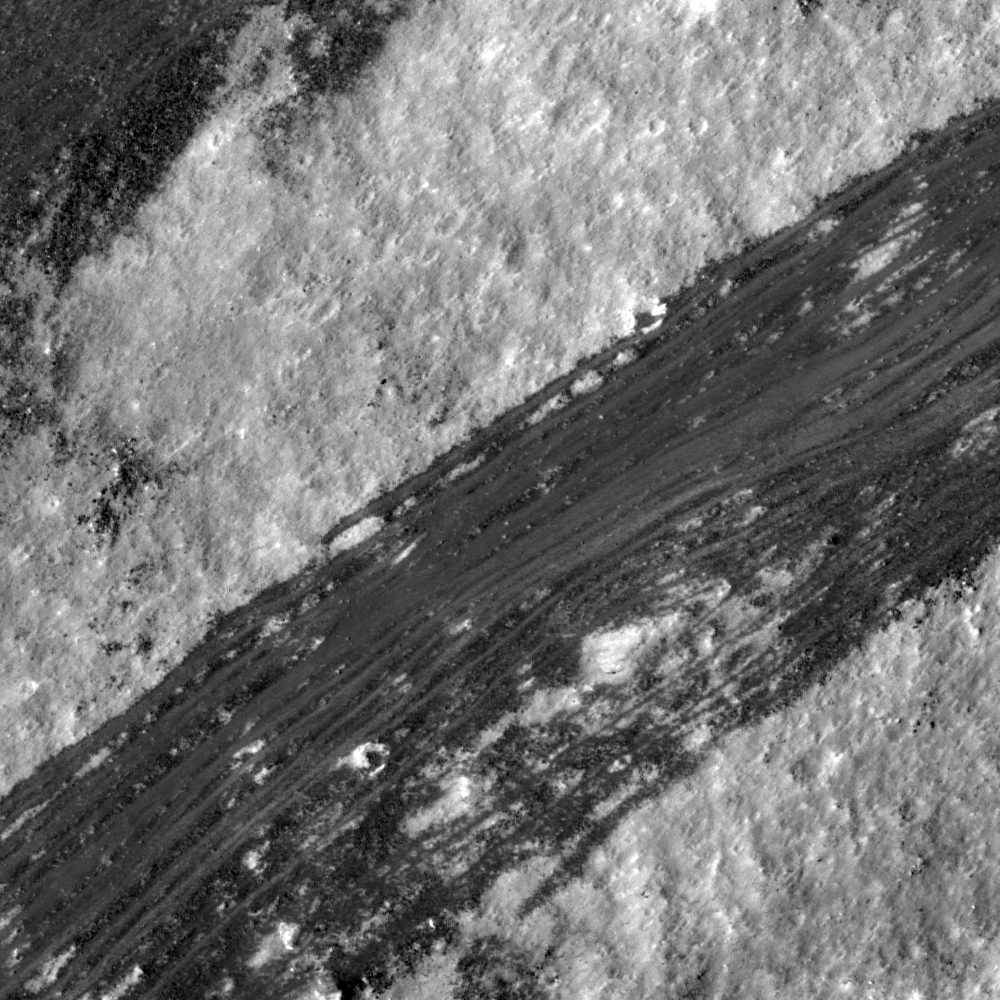

Dichotomy
Dark material on the wall of a Copernican crater. The center of the crater is to the lower left. Image number M135847041R, incidence angle 53°, image scale 0.53 m/pixel [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 24 Aug 2011
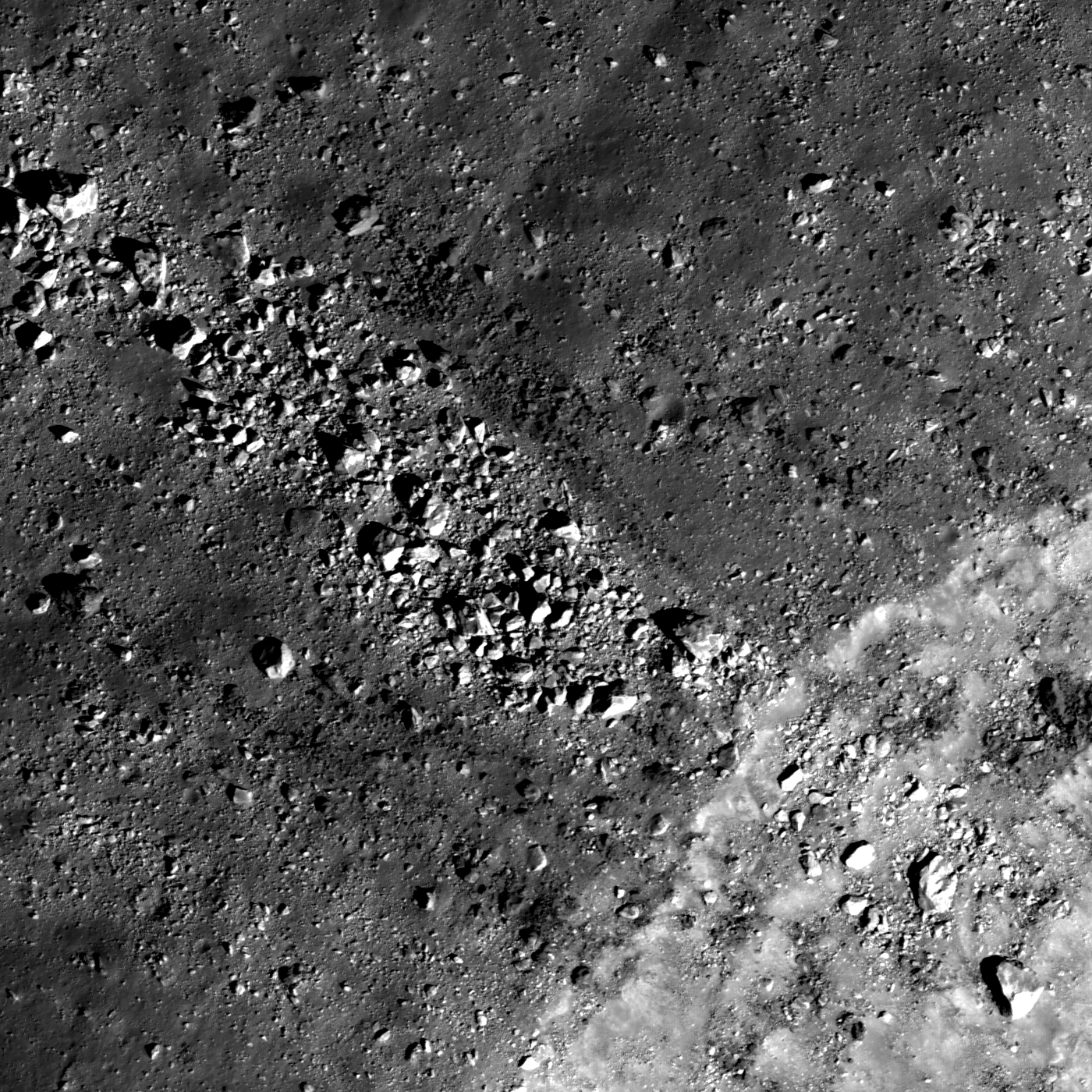

Ray of boulders
Dozens of boulders, ranging from 10 m to more than 30 m in diameter, are distributed within an ejecta ray close to the crater rim (lower right). These boulders represent the deepest material excavated during crater formation. LROC NAC...
Published on 18 Aug 2011
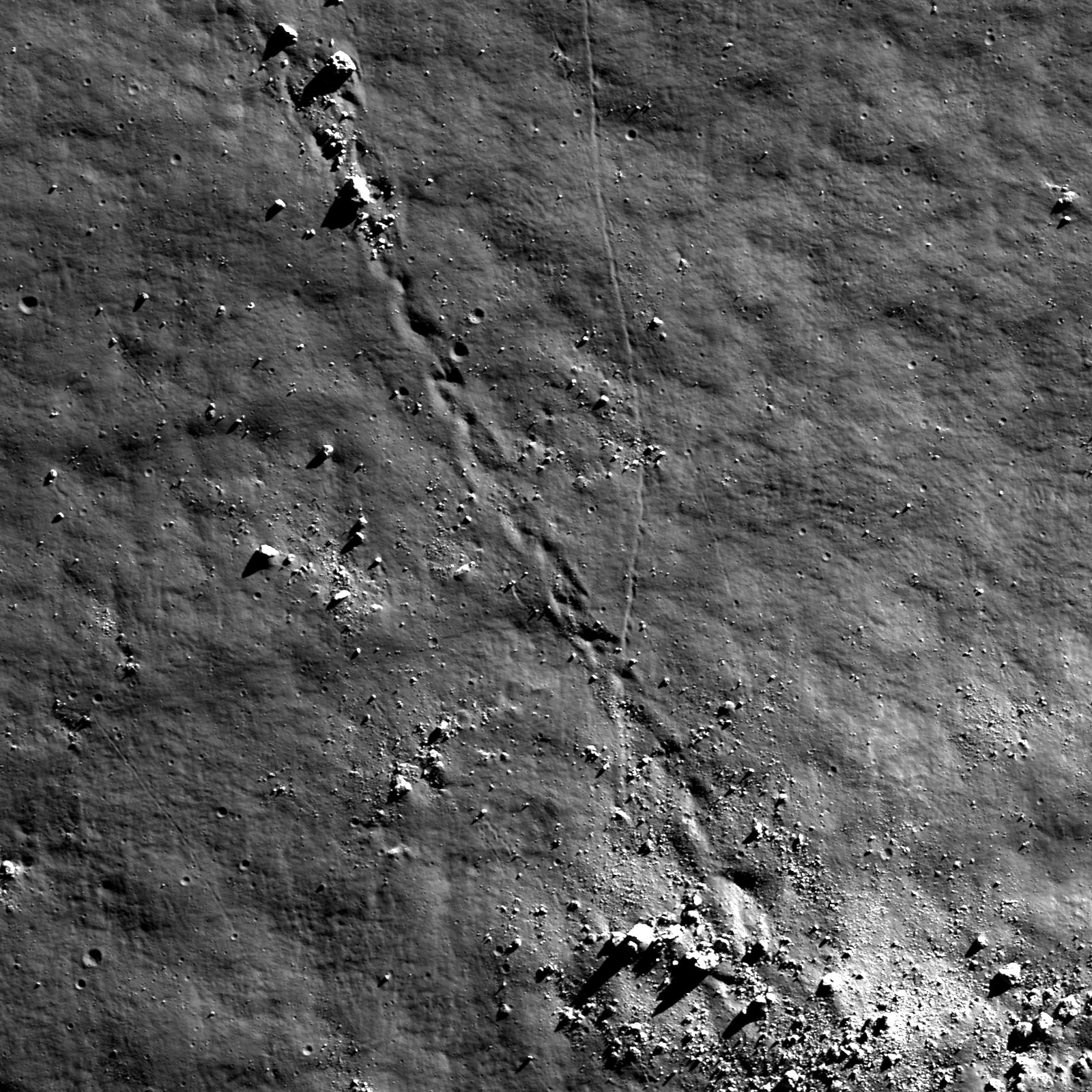

Sampling Schrödinger
Boulders rolled down an incline on a terrace near the Schrödinger basin rim. Boulders are ~20 to 30 m in size. Image width is ~1.2 km, downslope direction to upper left, LROC NAC M159017963R [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 17 Aug 2011
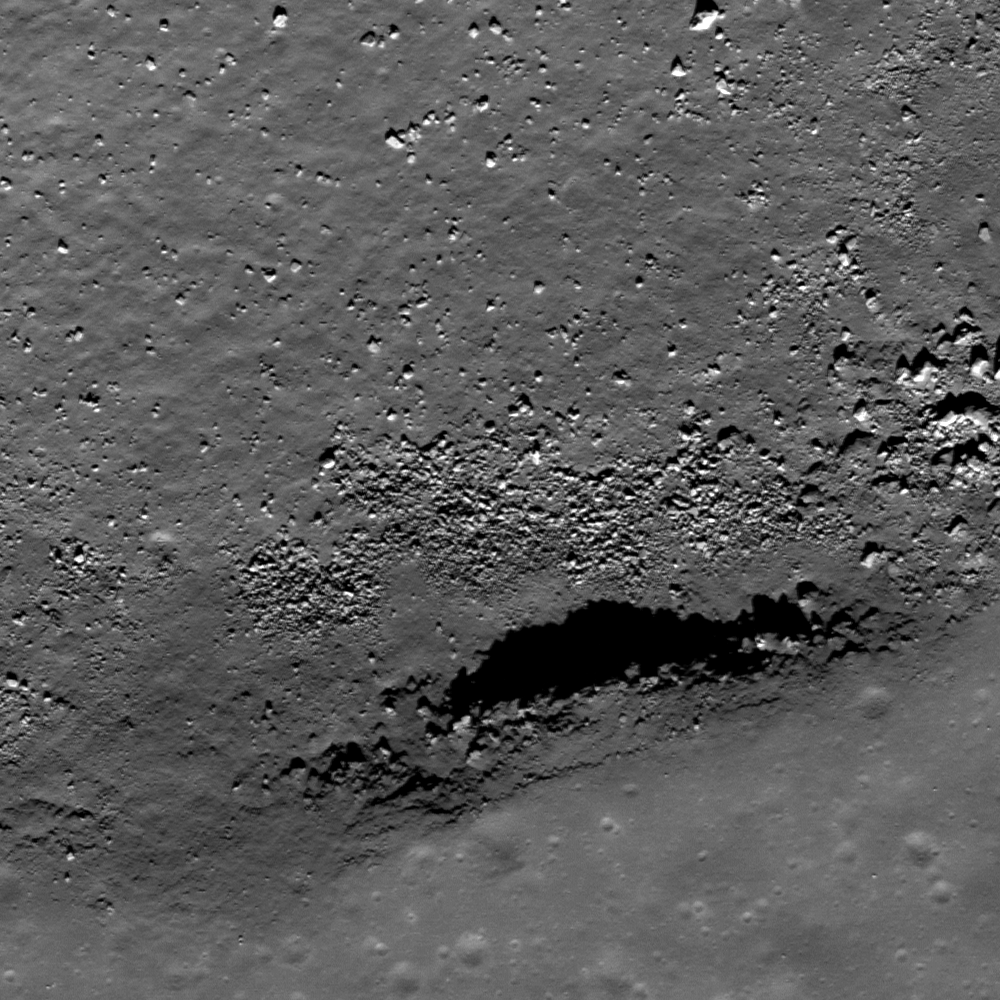

Lunar overhang?
Outcrop in the south wall of this unnamed rille may form an overhang. Image width 400 m across, LROC NAC M124790534R [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 16 Aug 2011
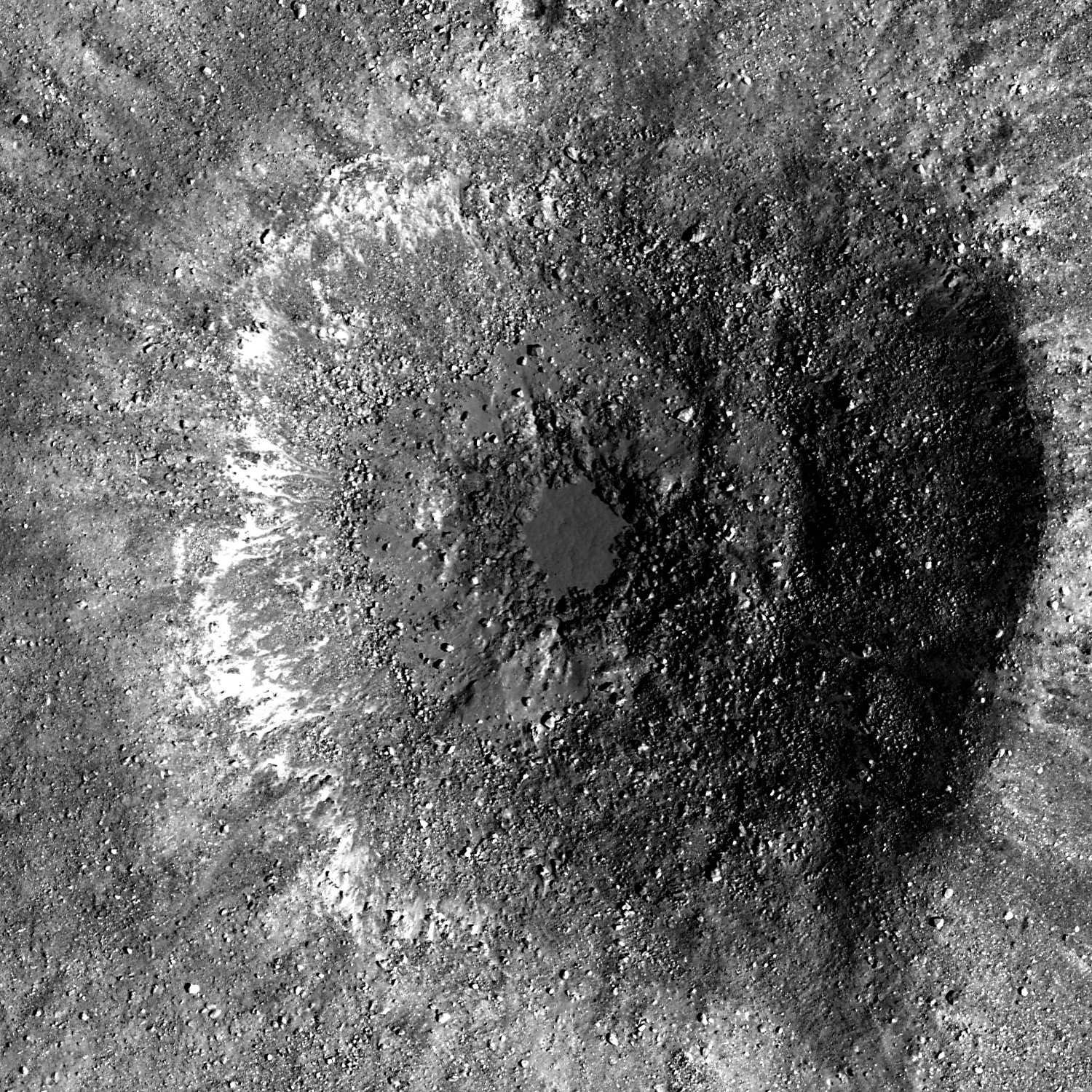

Recent Impact in Oceanus Procellarum
A small amount of impact melt pooled and froze on the floor of this Copernican impact crater, and is 90 x 70 m in size. What process creates impact melt pools? LROC NAC M111972680LE, image width is 750 m [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State...
Published on 12 Aug 2011
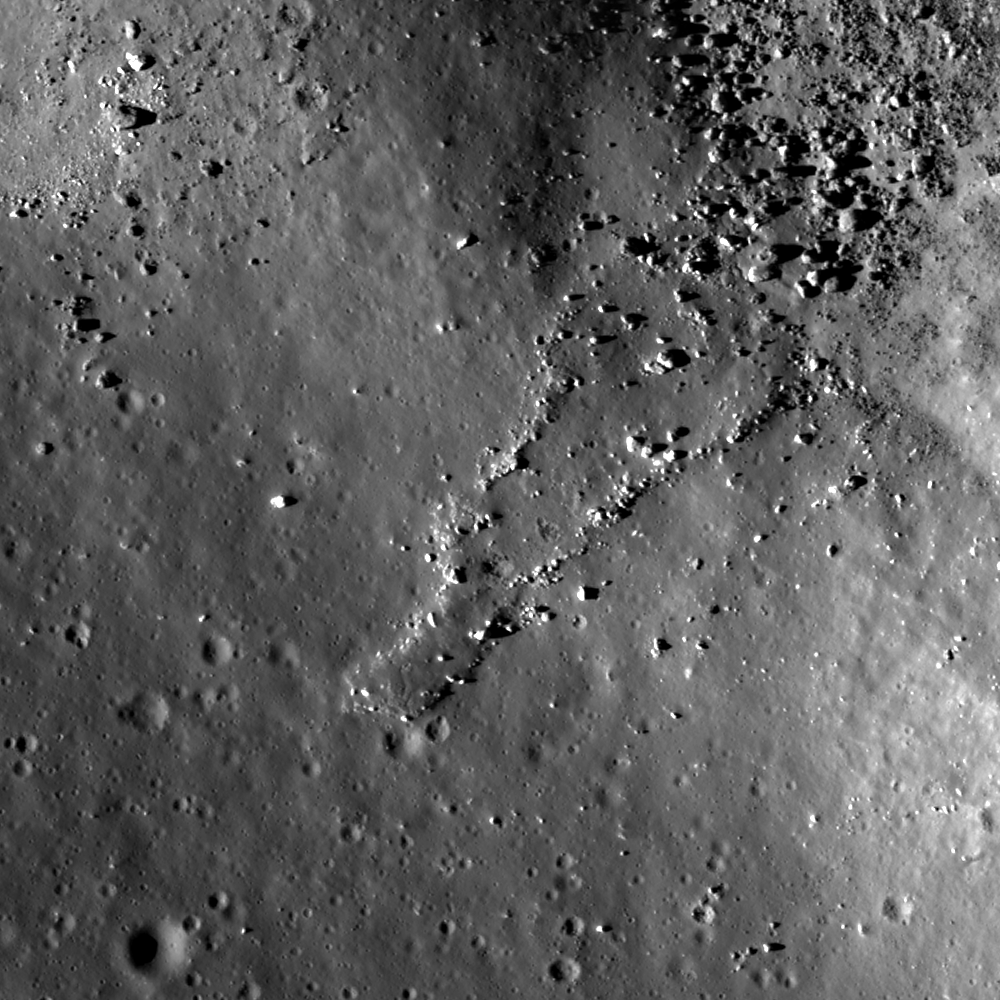

Impact melt tongue
A bouldery tongue of impact melt in Jackson crater. Image number M133892450L, incidence angle 75°, image scale 0.83 m/pixels [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 11 Aug 2011
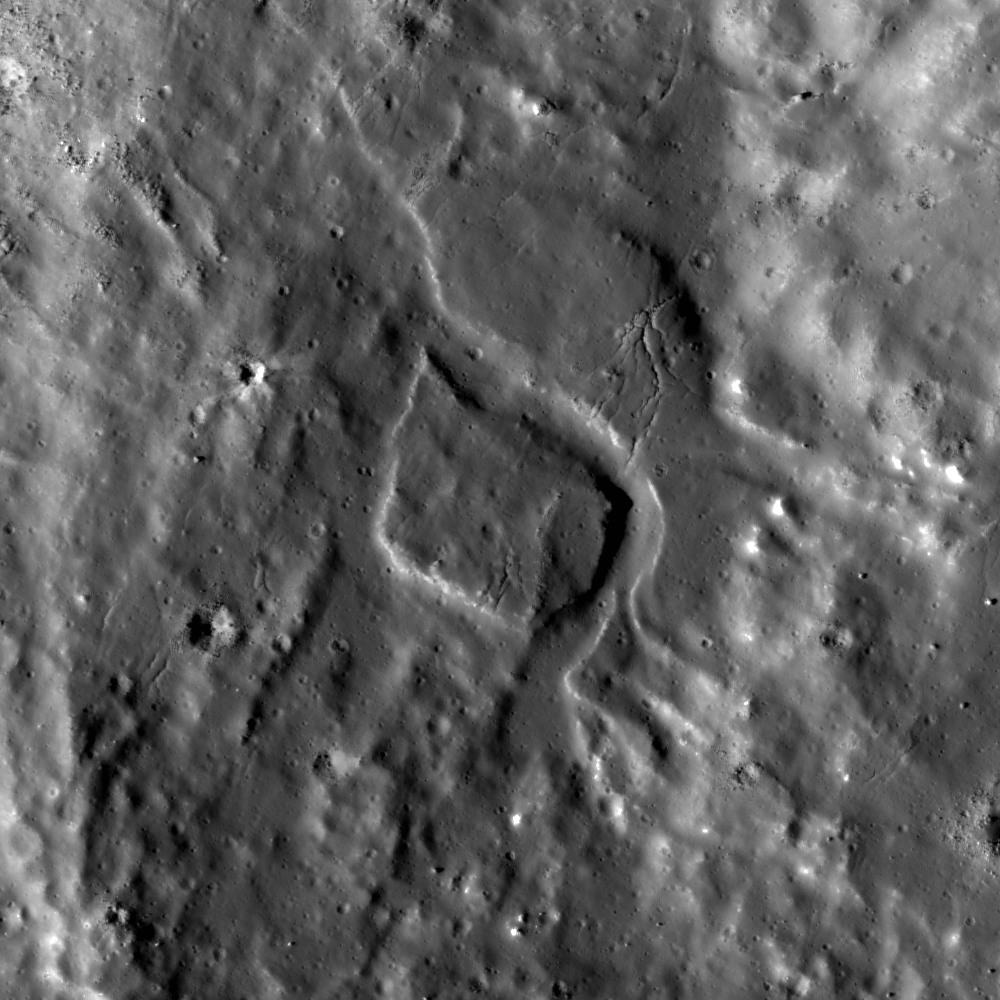

Channelized impact melt
Channelized impact melt flow cut through pre-existing rock. Image number M103216633L, incidence angle 68°, image scale 1.4 m/pixels, sunlight direction is from the left [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 10 Aug 2011
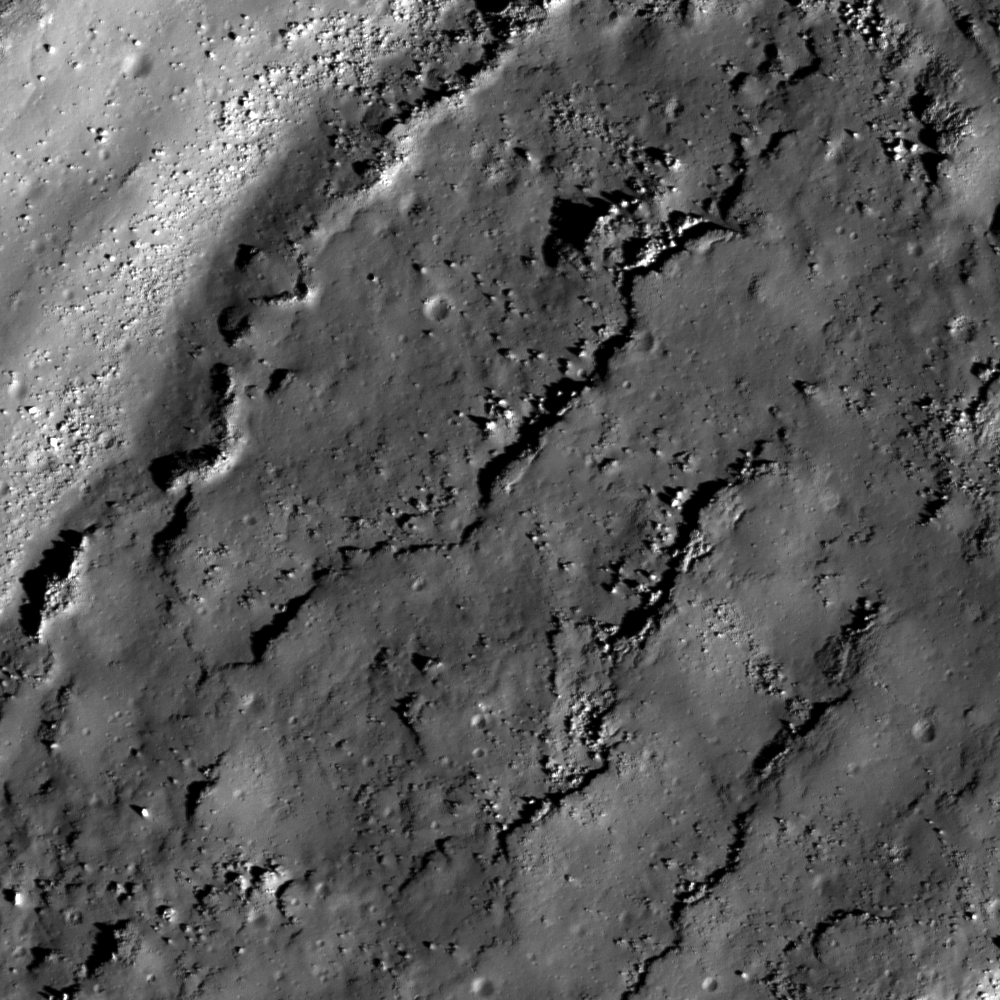

Waves
Waves of impact melt in Jackson crater. Sun direction is from the lower right hand corner. Image number M112658386R, incidence angle 46°, image scale 0.54 m/pixels [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 09 Aug 2011
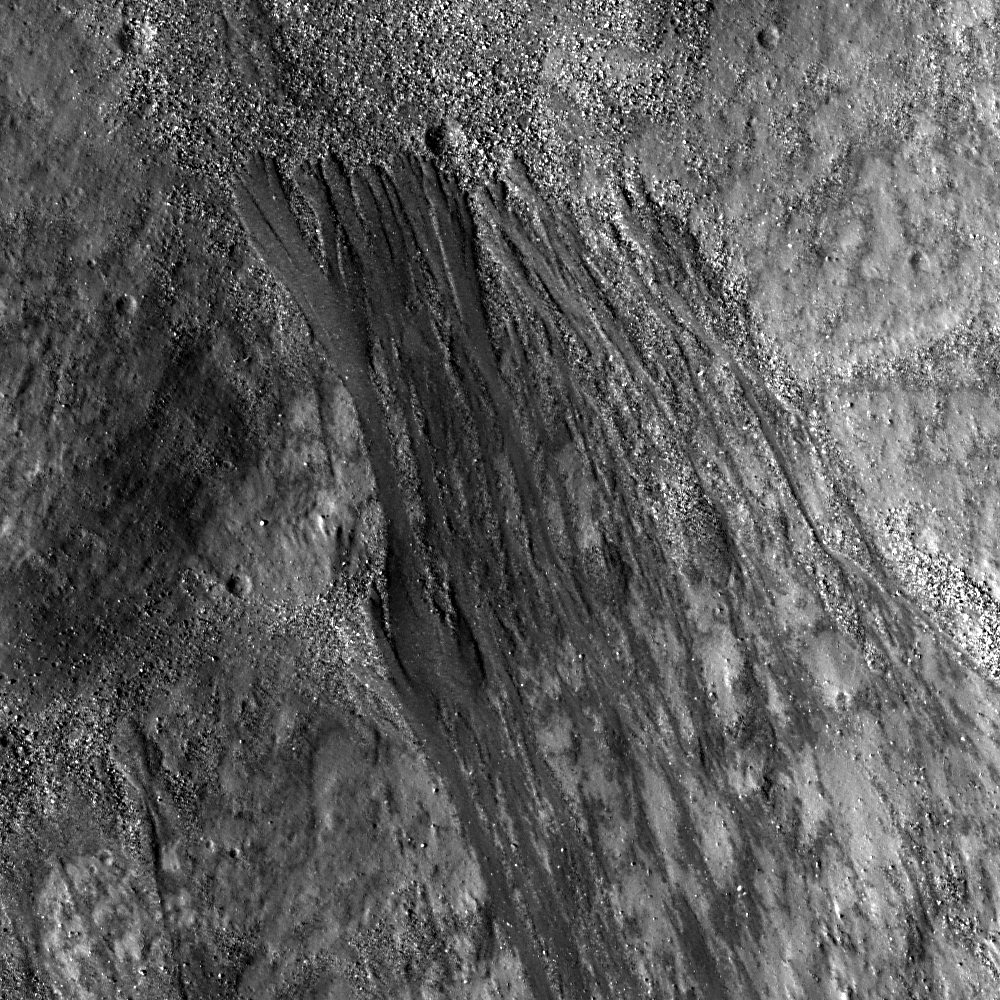

Tendrils in Reiner Crater
These elongate flows formed during their race towards the floor of Reiner crater. Boulders have piled up at the base of the flows. Are the flows impact melt, or something else? Downslope is to the upper left. LROC NAC M135548391LE,...
Published on 08 Aug 2011
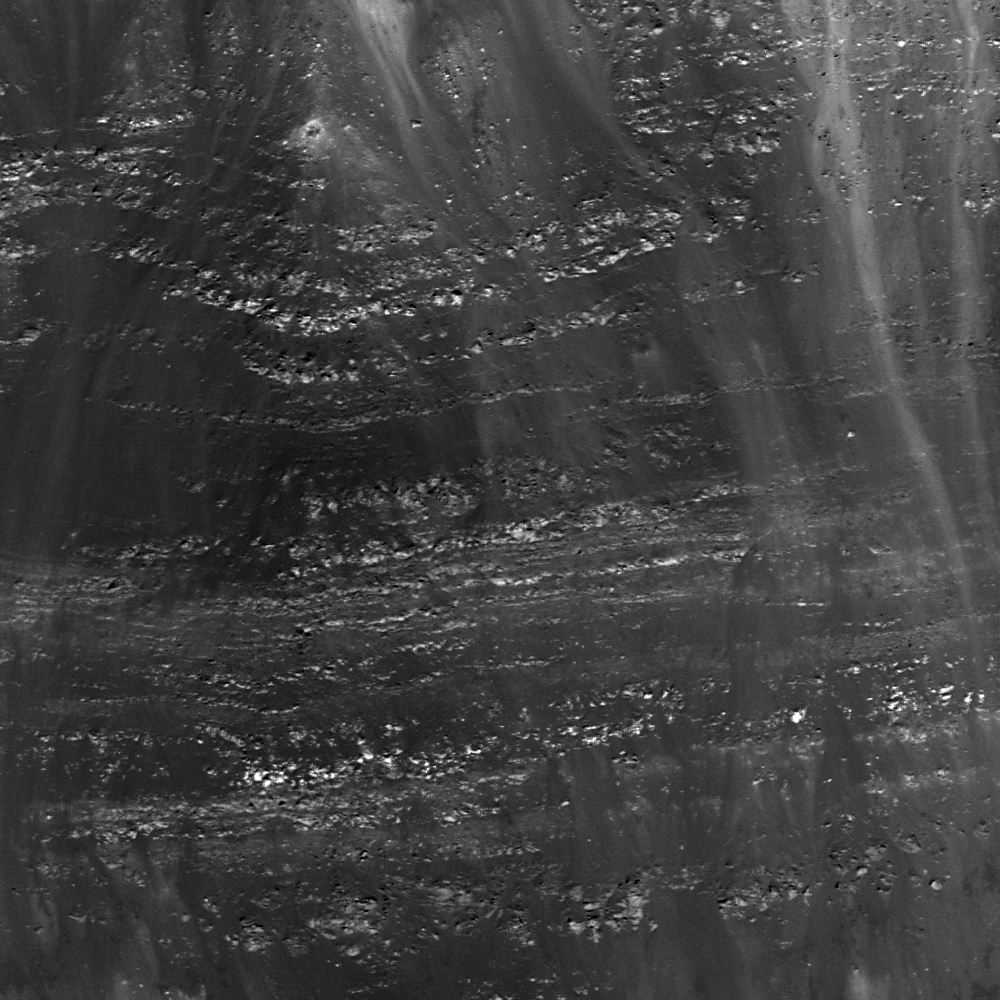

Layering in Euler Crater
Many layers are present in the wall of Euler crater. The layers are interpreted to be individual lava flows that formed the lunar maria. LROC NAC M124763045LE, image width is 500 m [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 02 Aug 2011
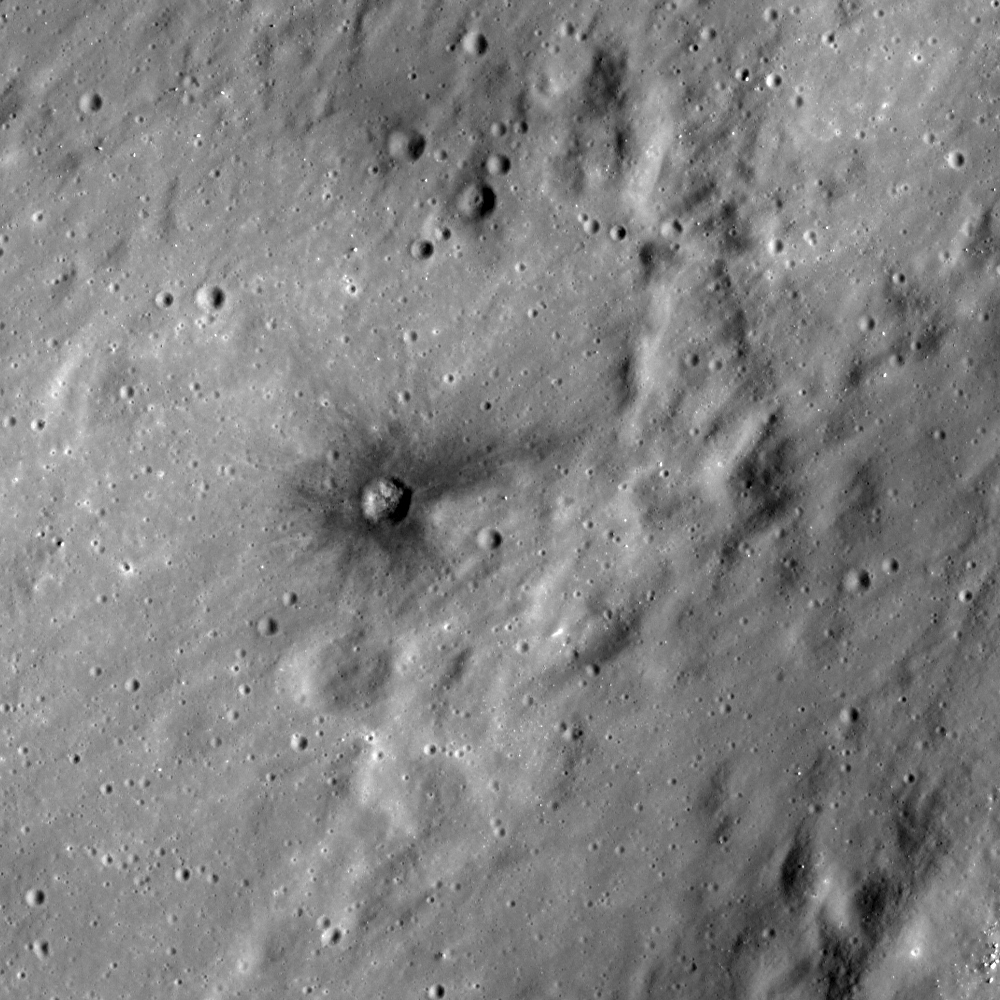

Dark halo crater
A small dark halo crater on the ejecta of Censorinus A crater. Image scale is 0.5 m/pixel, image width is 500m, incidence angle 45°, sunlight is from right side [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 28 Jul 2011
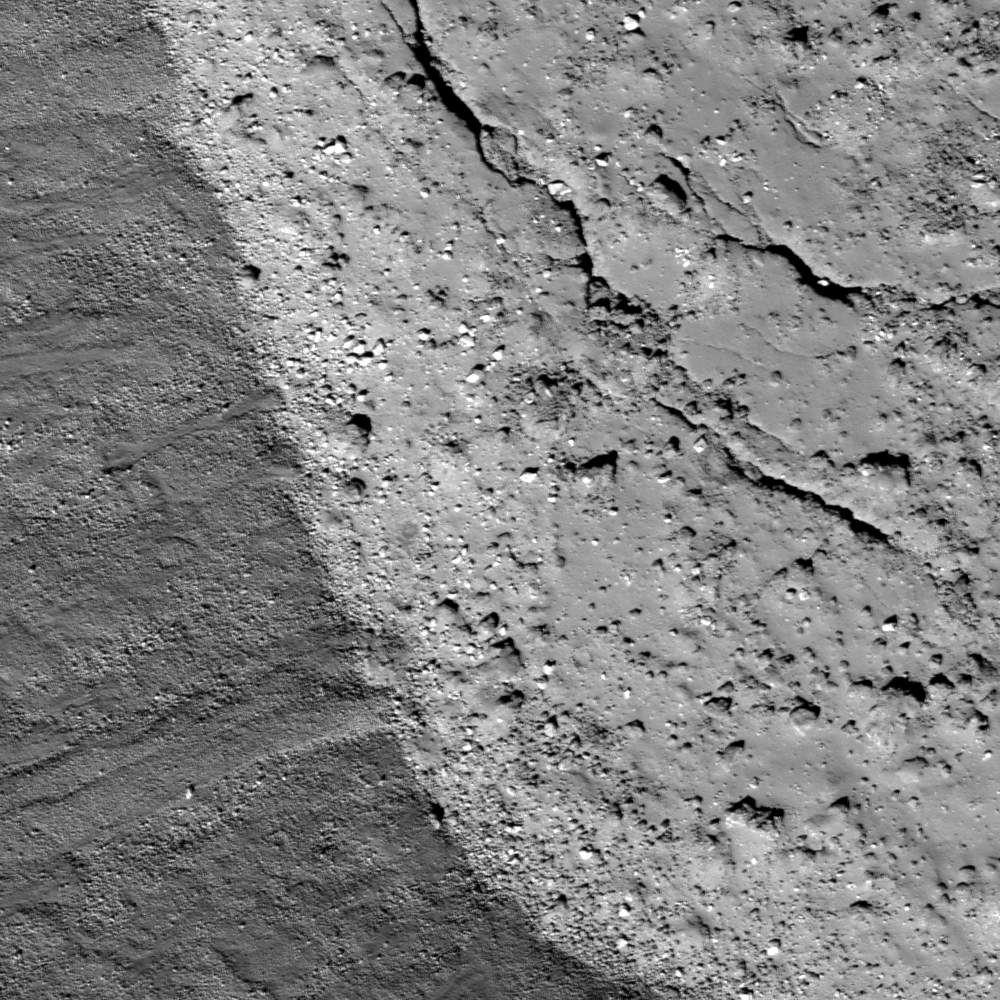

Melt and more melt
Southwestern edge of Rümker E crater floor. Image scale is 0.5 m/pixel, image width is 500m, incidence angle 43°, sunlight is from south-west [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 27 Jul 2011

Rootless impact melt flows
Impact melt flows extending out of Eimmart A crater. Image resolution is 0.5 m/pixel, image width is 500 m, incidence angle 44°, sunlight is from left [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 26 Jul 2011
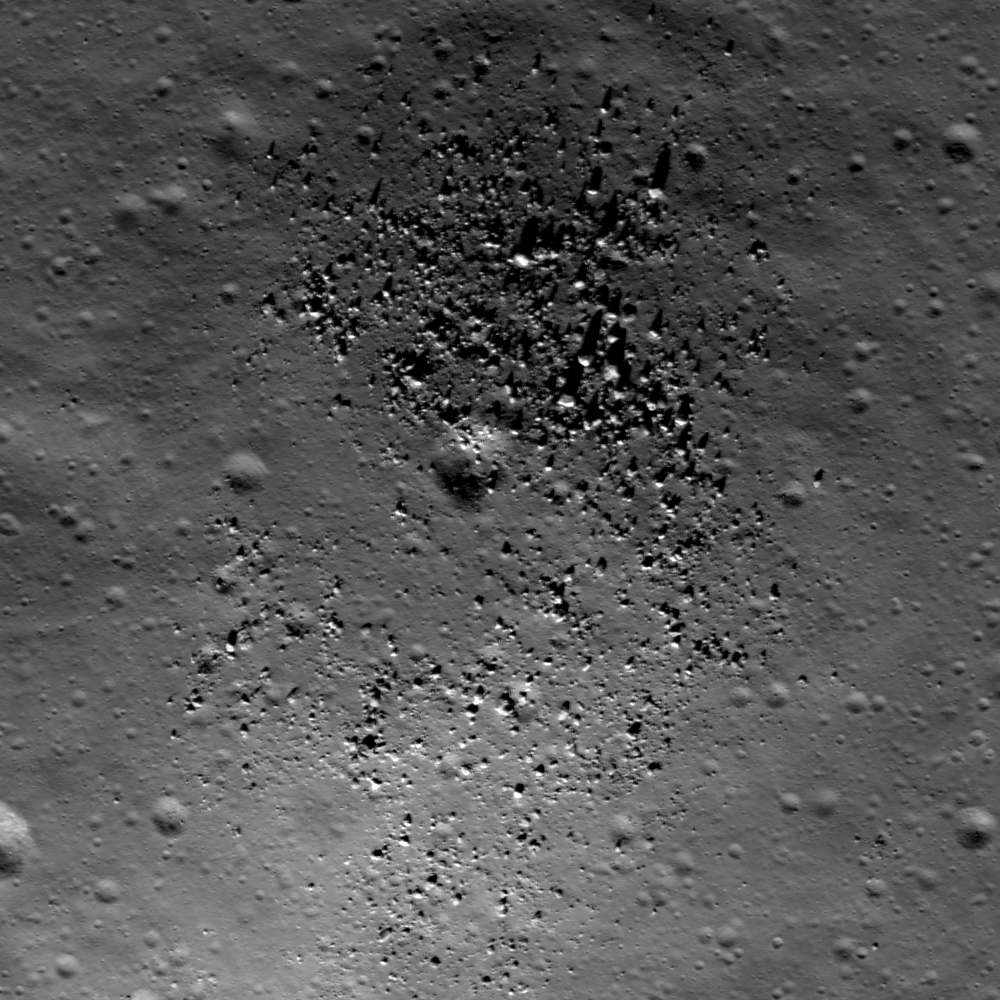

Farside Highlands Volcanism!
Small dome in the Compton-Belkovich region (61.33 °N, 99.68 °E). Evidence indicates a volcanic origin for this and other intriguing features in the region. Incidence angle is 64°, Sun is from the SSW, image is ~510 m across. NAC image...
Published on 25 Jul 2011
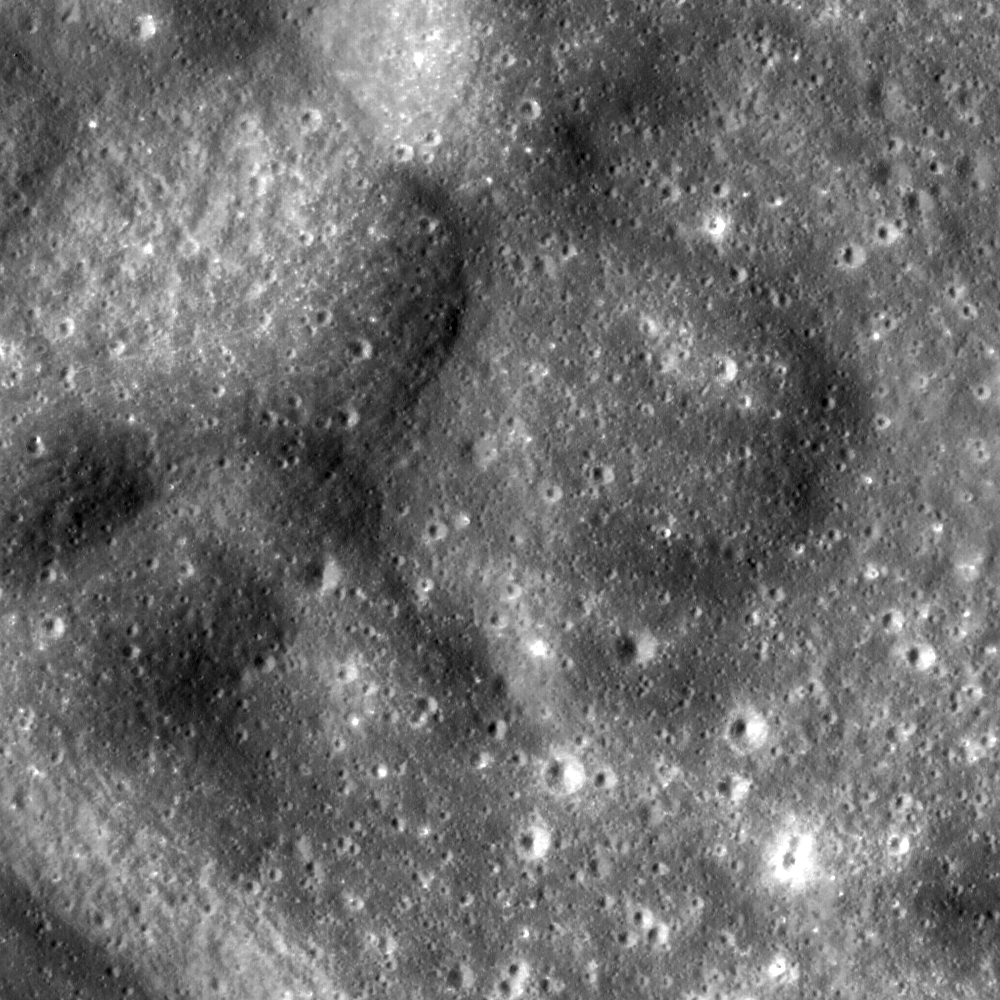
The Lavish Lobes of Necho R
What geologic process created these mounds (5.72°S, 122.09°E)? NAC image number M106074338R; incidence angle 35°, Sun is from the west, north is up, image is ~600 meters across [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 21 Jul 2011
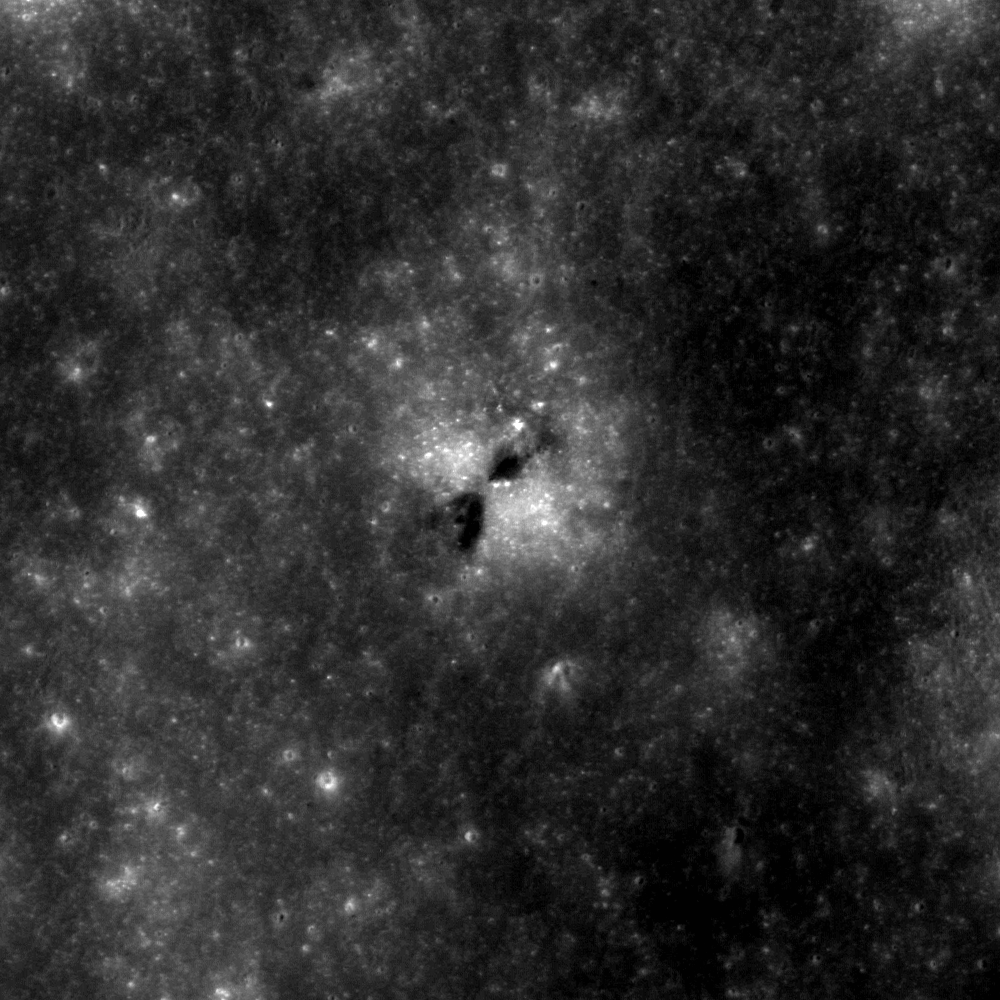

Crash or Coincidence?
An odd-looking impact feature raises an intriguing, Apollo-era trivia question (3.02°N, 119.15°E). NAC image number M141485413; incidence angle 12°; Sun is from the east; north is up; image is ~600 meters across [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State...
Published on 20 Jul 2011
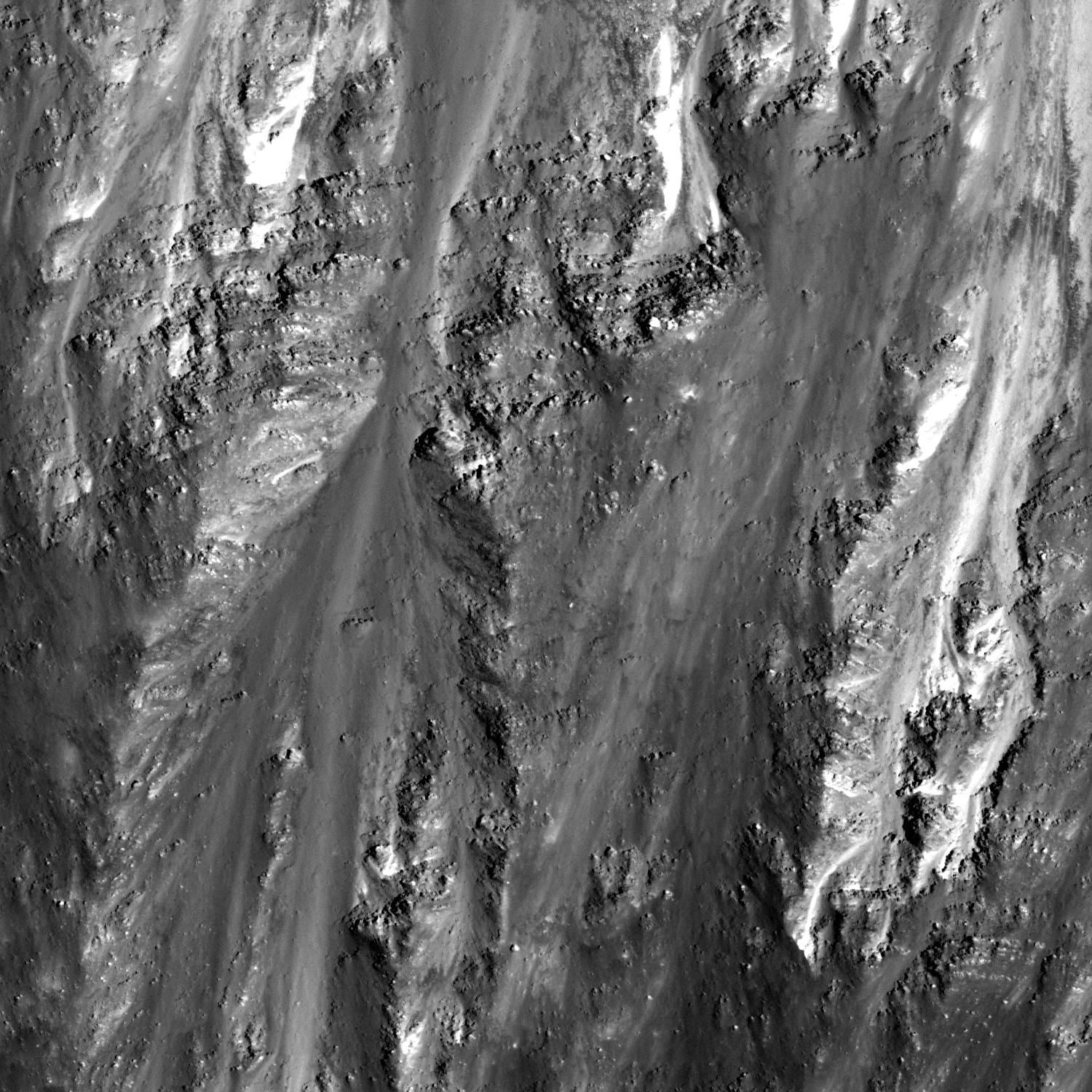
Layering in Messier A
Avalanches festoon the layered walls of Messier A crater (2.2°S, 46.9°E). NAC image number M126622485R, incidence angle 25°, Sun is from the east, north is up, image is ~625 meters across [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 19 Jul 2011

Splash and flow
Impact melt flowed across the primary ejecta of an unnamed Copernican-aged impact crater (46.75°N, 49.81°E). LROC NAC M159631206L,R; source crater toward the bottom [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 14 Jul 2011
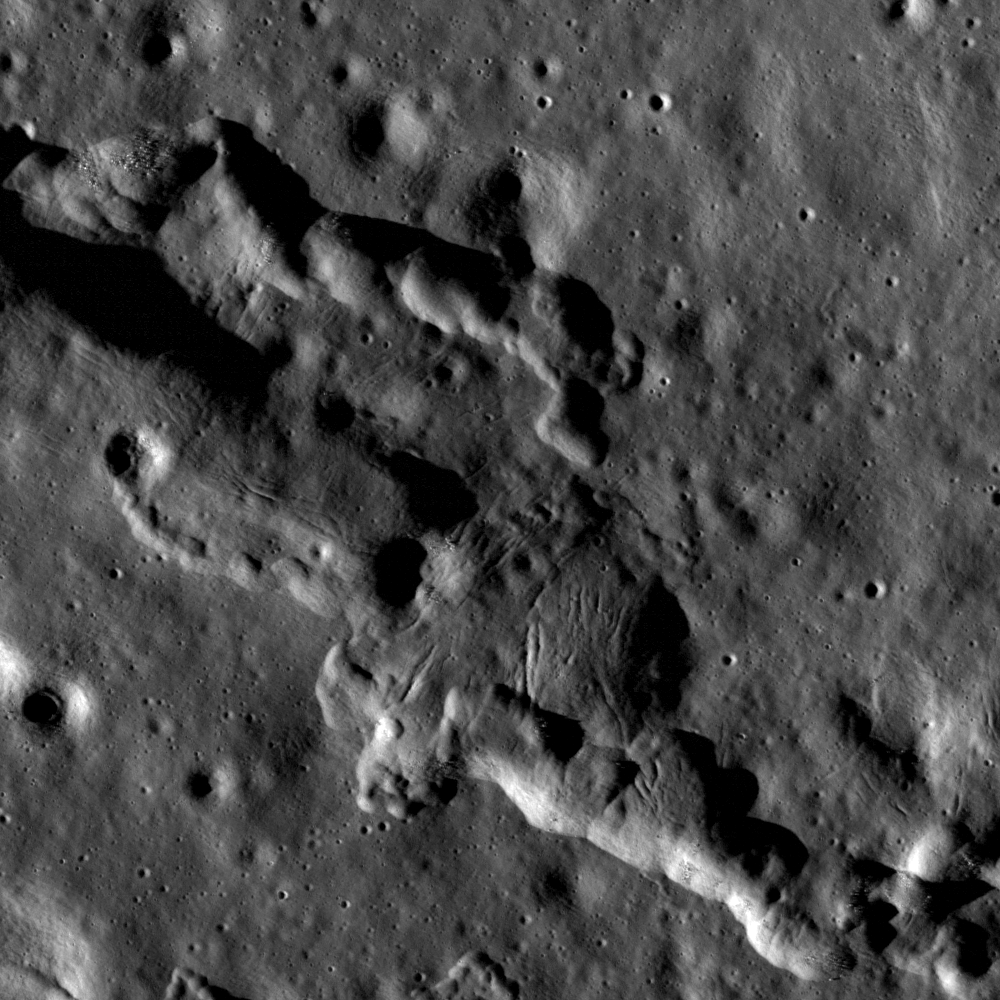

Stress and pull
Cracks - not boulders! - abound on the ridge crest of this wrinkle ridge in Mare Imbrium. LROC NAC M102171046LR, image width is 1.7 km [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].
Published on 13 Jul 2011